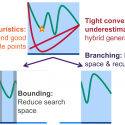
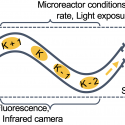
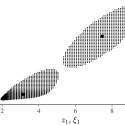
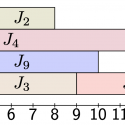
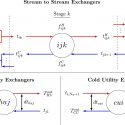
Dr Ruth Misener (she/her) is a Professor in the Computational Optimization Group, an Amazon Scholar, and the BASF/RAEng Research Chair in Data-Driven Optimization (2022-27). Foundations of her research are in numerical optimization and computational software. Her applications focus on optimization challenges arising in industry, e.g. in logistics or experimental design. Ruth also works at the interface of operations research and machine learning. Ruth’s research team develops open-source code on GitHub, releases video presentations on YouTube, and announces research on LinkedIn. See her inaugural lecture:
Dr Ruth Misener (she/her) is a Professor in the Computational Optimization Group, an Amazon Scholar, and the BASF/RAEng Research Chair in Data-Driven Optimization (2022-27). Foundations of her research are in numerical optimization and computational software. Her applications focus on optimization challenges arising in industry, e.g. in logistics or experimental design. Ruth also works at the interface of operations research and machine learning. Ruth’s research team develops open-source code on GitHub, releases video presentations on YouTube, and announces research on LinkedIn. See her inaugural lecture:
Ruth Misener
Optimization Models, Algorithms, and Software